11 WORKING WITH PUT REQUESTS
11 使用 PUT 请求
In this section, we are going to show you how to update a resource using the PUT request. We are going to update a child resource first and then we are going to show you how to execute insert while updating a parent resource.
在本节中,我们将向您展示如何使用 PUT 请求更新资源。我们将首先更新子资源,然后我们将向您展示如何在更新父资源时执行 insert。
11.1 Updating Employee
11.1 更新员工
In the previous sections, we first changed our interface, then the repository/service classes, and finally the controller. But for the update, this doesn’t have to be the case.
在前面的部分中,我们首先更改了接口,然后更改了存储库/服务类,最后更改了控制器。但对于更新,情况并非必须如此。
Let’s go step by step.
让我们一步一步来。
The first thing we are going to do is to create another DTO record for update purposes:
我们要做的第一件事是创建另一个 DTO 记录以进行更新:
public record EmployeeForUpdateDto(string Name, int Age, string Position);We do not require the Id property because it will be accepted through the URI, like with the DELETE requests. Additionally, this DTO contains the same properties as the DTO for creation, but there is a conceptual difference between those two DTO classes. One is for updating and the other is for creating. Furthermore, once we get to the validation part, we will understand the additional difference between those two.
我们不需要 Id 属性,因为它将通过 URI 接受,就像 DELETE 请求一样。此外,此 DTO 包含与用于创建的 DTO 相同的属性,但这两个 DTO 类之间存在概念差异。一个用于更新,另一个用于创建。此外,一旦我们进入验证部分,我们将了解这两者之间的额外区别。
Because we have an additional DTO record, we require an additional mapping rule:
因为我们有额外的 DTO 记录,所以我们需要额外的映射规则:
CreateMap<EmployeeForUpdateDto, Employee>();After adding the mapping rule, we can modify the IEmployeeService interface:
添加映射规则后,我们可以修改 IEmployeeService 接口:
using Shared.DataTransferObjects;
namespace Service.Contracts
{
public interface IEmployeeService
{
IEnumerable<EmployeeDto> GetEmployees(Guid companyId, bool trackChanges);
EmployeeDto GetEmployee(Guid companyId, Guid id, bool trackChanges);
EmployeeDto CreateEmployeeForCompany(Guid companyId, EmployeeForCreationDto employeeForCreation, bool trackChanges);
void DeleteEmployeeForCompany(Guid companyId, Guid id, bool trackChanges);
void UpdateEmployeeForCompany(Guid companyId, Guid id, EmployeeForUpdateDto employeeForUpdate, bool compTrackChanges, bool empTrackChanges);
}
}We are declaring a method that contains both id parameters – one for the company and one for employee, the employeeForUpdate object sent from the client, and two track changes parameters, again, one for the company and one for the employee. We are doing that because we won't track changes while fetching the company entity, but we will track changes while fetching the employee.
我们声明了一个包含两个 id 参数的方法 – 一个用于公司,一个用于员工,从客户端发送的 employeeForUpdate 对象,以及两个跟踪更改参数,同样,一个用于公司,一个用于员工。我们这样做是因为我们不会在获取公司实体时跟踪更改,但我们会在获取员工时跟踪更改。
That said, let’s modify the EmployeeService class:
也就是说,让我们修改 EmployeeService 类:
public void UpdateEmployeeForCompany(Guid companyId, Guid id, EmployeeForUpdateDto employeeForUpdate, bool compTrackChanges, bool empTrackChanges)
{
var company = _repository.Company.GetCompany(companyId, compTrackChanges);
if (company is null)
throw new CompanyNotFoundException(companyId);
var employeeEntity = _repository.Employee.GetEmployee(companyId, id, empTrackChanges);
if (employeeEntity is null)
throw new EmployeeNotFoundException(id);
_mapper.Map(employeeForUpdate, employeeEntity);
_repository.Save();
}So first, we fetch the company from the database. If it doesn’t exist, we interrupt the flow and send the response to the client. After that, we do the same thing for the employee. But there is one difference here. Pay attention to the way we fetch the company and the way we fetch the employeeEntity. Do you see the difference?
因此,首先,我们从数据库中获取公司。如果不存在,我们将中断流并将响应发送到客户端。之后,我们为员工做同样的事情。但这里有一个区别。注意我们获取 company 的方式以及我们获取 employeeEntity 的方式。您看到区别了吗?
As we’ve already said: the trackChanges parameter will be set to true for the employeeEntity. That’s because we want EF Core to track changes on this entity. This means that as soon as we change any property in this entity, EF Core will set the state of that entity to Modified.
正如我们已经说过的:employeeEntity 的 trackChanges 参数将设置为 true。这是因为我们希望 EF Core 跟踪此实体上的更改。这意味着,一旦我们更改此实体中的任何属性,EF Core 就会将该实体的状态设置为 Modified。
As you can see, we are mapping from the employeeForUpdate object (we will change just the age property in a request) to the employeeEntity — thus changing the state of the employeeEntity object to Modified.
如您所见,我们正在从 employeeForUpdate 对象(我们只更改请求中的 age 属性)映射到 employeeEntity,从而将 employeeEntity 对象的状态更改为 Modified。
Because our entity has a modified state, it is enough to call the Save method without any additional update actions. As soon as we call the Save method, our entity is going to be updated in the database.
由于我们的实体具有已修改的状态,因此调用 Save 方法就足够了,无需任何其他更新作。调用 Save 方法后,我们的实体将在数据库中更新。
Now, when we have all of these, let’s modify the EmployeesController:
现在,当我们拥有所有这些时,让我们修改 EmployeesController:
[HttpPut("{id:guid}")]
public IActionResult UpdateEmployeeForCompany(Guid companyId, Guid id, [FromBody] EmployeeForUpdateDto employee)
{
if (employee is null) return BadRequest("EmployeeForUpdateDto object is null");
_service.EmployeeService.UpdateEmployeeForCompany(companyId, id, employee, compTrackChanges: false, empTrackChanges: true);
return NoContent();
}We are using the PUT attribute with the id parameter to annotate this action. That means that our route for this action is going to be: api/companies/{companyId}/employees/{id}.
我们使用带有 id 参数的 PUT 属性来注释此作。这意味着此作的路由将为:api/companies/{companyId}/employees/{id}。
Then, we check if the employee object is null, and if it is, we return a BadRequest response.
然后,我们检查 employee 对象是否为 null,如果为 null,则返回 BadRequest 响应。
After that, we just call the update method from the service layer and pass false for the company track changes and true for the employee track changes.
之后,我们只需从服务层调用 update 方法,并为公司跟踪变化传递 false,为员工跟踪变化传递 true。
Finally, we return the 204 NoContent status.
最后,我们返回 204 NoContent 状态。
We can test our action:
我们可以测试我们的操作:
https://localhost:5001/api/companies/C9D4C053-49B6-410C-BC78-2D54A9991870/employees/80ABBCA8-664D-4B20-B5DE-024705497D4A
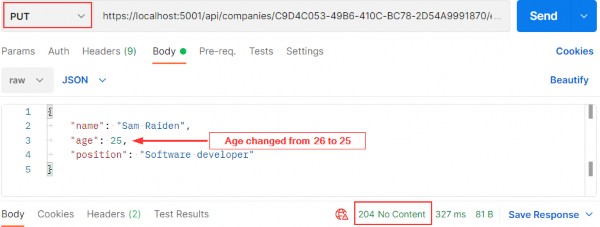
And it works; we get the 204 No Content status.
它奏效了;我们得到 204 No Content 状态。
We can check our executed query through EF Core to confirm that only the Age column is updated:
我们可以通过 EF Core 检查已执行的查询,以确认仅更新了 Age 列:
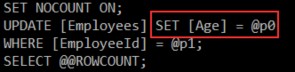
Excellent.
非常好。
You can send the same request with the invalid company id or employee id. In both cases, you should get a 404 response, which is a valid response to this kind of situation.
您可以使用无效的公司 ID 或员工 ID 发送相同的请求。在这两种情况下,您都应该得到 404 响应,这是对这种情况的有效响应。
NOTE: We’ve changed only the Age property, but we have sent all the other properties with unchanged values as well. Therefore, Age is only updated in the database. But if we send the object with just the Age property, other properties will be set to their default values and the whole object will be updated — not just the Age column. That’s because the PUT is a request for a full update. This is very important to know.
注意:我们只更改了 Age 属性,但我们也发送了值未更改的所有其他属性。因此,仅在数据库中更新 Age。但是,如果我们只发送具有 Age 属性的对象,则其他属性将设置为其默认值,并且整个对象将更新,而不仅仅是 Age 列。这是因为 PUT 是完全更新的请求。了解这一点非常重要。
11.1.1 About the Update Method from the RepositoryBase Class
11.1.1 关于 RepositoryBase 类中的 Update 方法
Right now, you might be asking: “Why do we have the Update method in the RepositoryBase class if we are not using it?”
现在,您可能会问:“如果我们不使用 Update 方法,为什么我们在 RepositoryBase 类中有它?
The update action we just executed is a connected update (an update where we use the same context object to fetch the entity and to update it). But sometimes we can work with disconnected updates. This kind of update action uses different context objects to execute fetch and update actions or sometimes we can receive an object from a client with the Id property set as well, so we don’t have to fetch it from the database. In that situation, all we have to do is to inform EF Core to track changes on that entity and to set its state to modified. We can do both actions with the Update method from our RepositoryBase class. So, you see, having that method is crucial as well.
我们刚刚执行的更新作是连接更新(我们使用相同的上下文对象来获取实体并更新它的更新)。但有时我们可以使用断开连接的更新。这种更新作使用不同的上下文对象来执行 fetch 和 update作,或者有时我们也可以从设置了 Id 属性的客户端接收对象,因此我们不必从数据库中获取它。在这种情况下,我们只需通知 EF Core 跟踪该实体的更改,并将其状态设置为 modified。我们可以使用 RepositoryBase 类中的 Update 方法执行这两个作。所以,你看,拥有这种方法也很重要。
One note, though. If we use the Update method from our repository, even if we change just the Age property, all properties will be updated in the database.
不过,有一点需要注意。如果我们使用存储库中的 Update 方法,即使我们只更改 Age 属性,所有属性都将在数据库中更新。
11.2 Inserting Resources while Updating One
11.2 在更新资源时插入资源
While updating a parent resource, we can create child resources as well without too much effort. EF Core helps us a lot with that process. Let’s see how.
在更新父资源时,我们也可以创建子资源,而无需太多工作。EF Core 在此过程中为我们提供了很大帮助。让我们看看如何作。
The first thing we are going to do is to create a DTO record for update:
我们要做的第一件事是创建一个用于更新的 DTO 记录:
public record CompanyForUpdateDto(string Name, string Address, string Country, IEnumerable<EmployeeForCreationDto> Employees);After this, let’s create a new mapping rule:
在此之后,让我们创建一个新的映射规则:
CreateMap<CompanyForUpdateDto, Company>();Then, let’s move on to the interface modification:
然后,让我们继续进行接口修改:
using Shared.DataTransferObjects;
namespace Service.Contracts
{
public interface ICompanyService
{
IEnumerable<CompanyDto> GetAllCompanies(bool trackChanges);
CompanyDto GetCompany(Guid companyId, bool trackChanges);
CompanyDto CreateCompany(CompanyForCreationDto company);
IEnumerable<CompanyDto> GetByIds(IEnumerable<Guid> ids, bool trackChanges);
(IEnumerable<CompanyDto> companies, string ids) CreateCompanyCollection(IEnumerable<CompanyForCreationDto> companyCollection);
void DeleteCompany(Guid companyId, bool trackChanges);
void UpdateCompany(Guid companyid, CompanyForUpdateDto companyForUpdate, bool trackChanges);
}
}
And of course, the service class modification:
当然,服务类修改:
public void UpdateCompany(Guid companyId, CompanyForUpdateDto companyForUpdate, bool trackChanges)
{
var companyEntity = _repository.Company.GetCompany(companyId, trackChanges);
if (companyEntity is null)
throw new CompanyNotFoundException(companyId);
_mapper.Map(companyForUpdate, companyEntity);
_repository.Save();
}So again, we fetch our company entity from the database, and if it is null, we just return the NotFound response. But if it’s not null, we map the companyForUpdate DTO to companyEntity and call the Save method.
因此,我们从数据库中获取我们的公司实体,如果它是 null,我们只返回 NotFound 响应。但如果它不为 null,我们将 companyForUpdate DTO 映射到 companyEntity 并调用 Save 方法。
Right now, we can modify our controller:
现在,我们可以修改我们的控制器:
[HttpPut("{id:guid}")]
public IActionResult UpdateCompany(Guid id, [FromBody] CompanyForUpdateDto company)
{
if (company is null)
return BadRequest("CompanyForUpdateDto object is null");
_service.CompanyService.UpdateCompany(id, company, trackChanges: true);
return NoContent();
}That’s it. You can see that this action is almost the same as the employee update action.
就是这样。您可以看到,此作与 employee update作几乎相同。
Let’s test this now:
现在让我们测试一下:
https://localhost:5001/api/companies/3d490a70-94ce-4d15-9494-5248280c2ce3i
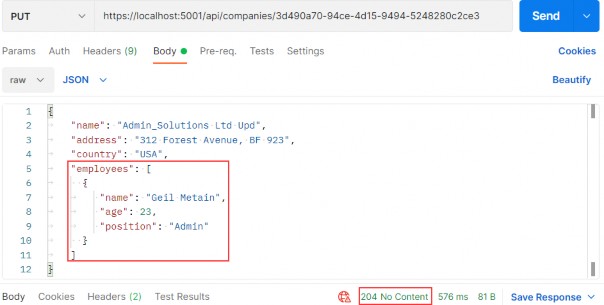
We modify the name of the company and attach an employee as well. As a result, we can see 204, which means that the entity has been updated. But what about that new employee?
我们修改公司名称并附加员工。结果,我们可以看到 204,这意味着该实体已更新。但是那位新员工呢?
Let’s inspect our query:
我们来检查一下我们的查询:
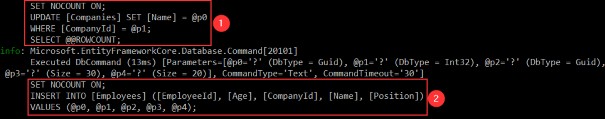
You can see that we have created the employee entity in the database. So, EF Core does that job for us because we track the company entity. As soon as mapping occurs, EF Core sets the state for the company entity to modified and for all the employees to added. After we call the Save method, the Name property is going to be modified and the employee entity is going to be created in the database.
您可以看到我们已经在数据库中创建了 employee 实体。因此,EF Core 为我们完成了这项工作,因为我们跟踪公司实体。映射发生后,EF Core 会将公司实体的状态设置为 modified,并将所有员工的状态设置为 added。调用 Save 方法后,将修改 Name 属性,并在数据库中创建 employee 实体。
We are finished with the PUT requests, so let’s continue with PATCH.
我们已经完成了 PUT 请求,所以让我们继续 PATCH。