15 Generating responses with page handlers in Razor Pages
15 在 Razor Pages 中使用页面处理程序生成响应
This chapter covers
本章涵盖
• Selecting which page handler in a Razor Page to invoke for a request
选择要为请求调用的 Razor 页面中的页面处理程序
• Returning an IActionResult from a page handler
从页面处理程序返回 IActionResult
• Handling status code errors with StatusCodePagesMiddleware
使用 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 处理状态代码错误
In chapter 14 you learned how the routing system selects a Razor Page to execute based on its associated route template and the request URL, but each Razor Page can have multiple page handlers. In this chapter you’ll learn all about page handlers, their responsibilities, and how a single Razor Page selects which handler to execute for a request.
在第 14 章中,你了解了路由系统如何根据其关联的路由模板和请求 URL 选择要执行的 Razor 页面,但每个 Razor 页面可以有多个页面处理程序。在本章中,您将了解有关页面处理程序、其职责以及单个 Razor 页面如何为请求选择要执行的处理程序的所有信息。
In section 15.3 we look at some of the ways of retrieving values from an HTTP request in a page handler. Much like minimal APIs, page handlers can accept method arguments that are bound to values in the HTTP request, but Razor Pages can also bind the request to properties on the PageModel.
在 Section 15.3 中,我们了解了在页面处理程序中从 HTTP 请求中检索值的一些方法。与最小 API 非常相似,页面处理程序可以接受绑定到 HTTP 请求中值的方法参数,但 Razor Pages 也可以将请求绑定到 PageModel 上的属性。
In section 15.4 you’ll learn how to return IActionResult objects from page handlers. Then you look at some of the common IActionResult types that you’ll return from page handlers for generating HTML and redirect responses.
在第 15.4 节中,您将学习如何从页面处理程序返回 IActionResult 对象。然后,您查看将从页面处理程序返回的一些常见 IActionResult 类型,这些类型用于生成 HTML 和重定向响应。
Finally, in section 15.5 you’ll learn how to use the StatusCodePagesMiddleware to improve the error status code responses in your middleware pipeline. This middleware intercepts error responses such as basic 404 responses and reexecutes the middleware pipeline to generate a pretty HTML response for the error. This gives users a much nicer experience when they encounter an error browsing your Razor Pages app.
最后,在 15.5 节中,您将学习如何使用 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 来改进中间件管道中的错误状态代码响应。此中间件会拦截错误响应(例如基本的 404 响应),并重新执行中间件管道以生成错误的漂亮 HTML 响应。当用户在浏览 Razor Pages 应用程序时遇到错误时,这为他们提供了更好的体验。
We’ll start by taking a quick look at the responsibilities of a page handler before we move on to see how the Razor Page infrastructure selects which page handler to execute.
首先,我们将快速了解页面处理程序的职责,然后再继续了解 Razor Page 基础结构如何选择要执行的页面处理程序。
15.1 Razor Pages and page handlers
15.1 Razor 页面和页面处理程序
In chapter 13 I described the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern and showed how it relates to ASP.NET Core. In this design pattern, the “controller” receives a request and is the entry point for UI generation. For Razor Pages, the entry point is the page handler that resides in a Razor Page’s PageModel. A page handler is a method that runs in response to a request.
在第 13 章中,我介绍了模型-视图-控制器 (MVC) 设计模式,并展示了它与 ASP.NET Core 的关系。在此设计模式中,“控制器” 接收请求,并且是生成 UI 的入口点。对于 Razor 页面,入口点是驻留在 Razor 页面的 PageModel 中的页面处理程序。页面处理程序是为响应请求而运行的方法。
The responsibility of a page handler is generally threefold:
页面处理程序的责任通常有三个方面:
• Confirm that the incoming request is valid.
确认传入请求有效。
• Invoke the appropriate business logic corresponding to the incoming request.
调用与传入请求对应的适当业务逻辑。
• Choose the appropriate kind of response to return.
选择要返回的适当响应类型。
A page handler doesn’t need to perform all these actions, but at the very least it must choose the kind of response to return. Page handlers typically return one of three things:
页面处理程序不需要执行所有这些作,但至少它必须选择要返回的响应类型。页面处理程序通常返回以下三项内容之一:
• A PageResult object—This causes the associated Razor view to generate an HTML response.
PageResult 对象 - 这会导致关联的 Razor 视图生成 HTML 响应。
• Nothing (the handler returns void or Task)—This is the same as the previous case, causing the Razor view to generate an HTML response.
Nothing (处理程序返回 void 或 Task) - 这与前一种情况相同,会导致 Razor 视图生成 HTML 响应。
• A RedirectToPageResult—This indicates that the user should be redirected to a different page in your application.
RedirectToPageResult - 这表示应将用户重定向到应用程序中的其他页面。
These are the most common results for Razor Pages, but I describe some additional options in section 15.4.
这些是 Razor Pages 最常见的结果,但我会在第 15.4 节中介绍一些其他选项。
It’s important to realize that a page handler doesn’t generate a response directly; it selects the type of response and prepares the data for it. For example, returning a PageResult doesn’t generate any HTML at that point; it merely indicates that a view should be rendered. This is in keeping with the MVC design pattern in which it’s the view that generates the response, not the controller.
请务必认识到,页面处理程序不会直接生成响应;它选择响应的类型并为其准备数据。例如,返回 PageResult 此时不会生成任何 HTML;它仅指示应呈现视图。这与 MVC 设计模式一致,在这种模式中,生成响应的是视图,而不是控制器。
Tip The page handler is responsible for choosing what sort of response to send; the view engine in the MVC framework uses the result to generate the response.
提示:页面处理程序负责选择要发送的响应类型;MVC 框架中的视图引擎使用结果生成响应。
It’s also worth bearing in mind that page handlers generally shouldn’t be performing business logic directly. Instead, they should call appropriate services in the application model to handle requests. If a page handler receives a request to add a product to a user’s cart, it shouldn’t manipulate the database or recalculate cart totals directly, for example. Instead, it should make a call to another class to handle the details. This approach of separating concerns ensures that your code stays testable and maintainable as it grows.
还值得记住的是,页面处理程序通常不应直接执行业务逻辑。相反,它们应该调用应用程序模型中的相应服务来处理请求。例如,如果页面处理程序收到将产品添加到用户购物车的请求,则它不应直接作数据库或重新计算购物车总数。相反,它应该调用另一个类来处理细节。这种分离关注点的方法可确保您的代码在增长过程中保持可测试性和可维护性。
15.2 Selecting a page handler to invoke
15.2 选择要调用的页面处理程序
In chapter 14 I said routing is about mapping URLs to an endpoint, which for Razor Pages means a page handler. But I’ve mentioned several times that Razor Pages can contain multiple page handlers. In this section you’ll learn how the EndpointMiddleware selects which page handler to invoke when it executes a Razor Page.
在第 14 章中,我说路由是将 URL 映射到端点,对于 Razor Pages 来说,端点是指页面处理程序。但我已多次提到 Razor Pages 可以包含多个页面处理程序。在本部分中,你将了解 EndpointMiddleware 如何在执行 Razor 页面时选择要调用的页面处理程序。
As you saw in chapter 14, the path of a Razor Page on disk controls the default route template for a Razor Page. For example, the Razor Page at the path Pages/Products/Search.cshtml has a default route template of Products/Search. When a request is received with the URL /products/search, the RoutingMiddleware selects this Razor Page, and the request passes through the middleware pipeline to the EndpointMiddleware. At this point, the EndpointMiddleware must choose which page handler to execute, as shown in figure 15.1.
如第 14 章所示,磁盘上 Razor 页面的路径控制 Razor 页面的默认路由模板。例如,路径 Pages/Products/Search.cshtml 处的 Razor 页面具有 Products/Search 的默认路由模板。当收到 URL 为 /products/search 的请求时,RoutingMiddleware 会选择此 Razor 页面,并且请求通过中间件管道传递到 EndpointMiddleware。此时,EndpointMiddleware 必须选择要执行的页面处理程序,如图 15.1 所示。
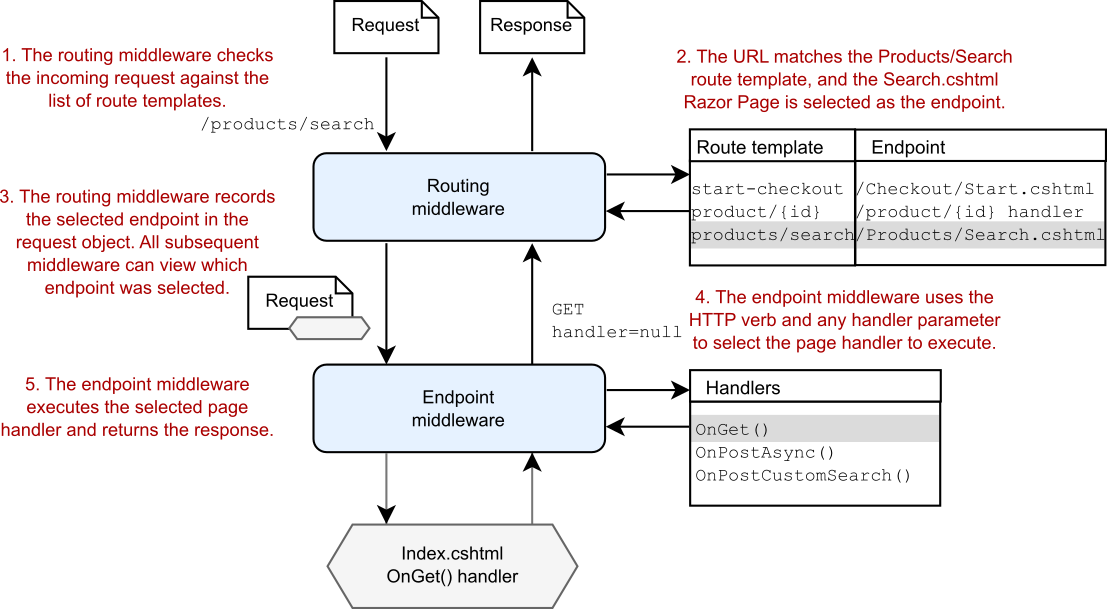
Figure 15.1 The routing middleware selects the Razor Page to execute based on the incoming request URL. Then the endpoint middleware selects the endpoint to execute based on the HTTP verb of the request and the presence (or lack) of a handler route value.
图 15.1 路由中间件根据传入请求 URL 选择要执行的 Razor 页面。然后,端点中间件根据请求的 HTTP 动词和处理程序路由值的存在(或缺失)选择要执行的端点。
Consider the Razor Page SearchModel shown in listing 15.1. This Razor Page has three handlers: OnGet, OnPostAsync, and OnPostCustomSearch. The bodies of the handler methods aren’t shown, as we’re interested only in how the EndpointMiddleware chooses which handler to invoke.
请考虑清单 15.1 中所示的 Razor Page SearchModel。此 Razor 页面有三个处理程序:OnGet、OnPostAsync 和 OnPostCustomSearch。处理程序方法的主体没有显示,因为我们只对 EndpointMiddleware 如何选择要调用的处理程序感兴趣。
Listing 15.1 Razor Page with multiple page handlers
列表 15.1 具有多个页面处理程序的 Razor Page
public class SearchModel : PageModel
{
public void OnGet() ❶
{
// Handler implementation
}
public Task OnPostAsync() ❷
{
// Handler implementation
}
public void OnPostCustomSearch() ❸
{
// Handler implementation
}
}❶ Handles GET requests
处理 GET 请求
❷ Handles POST requests. The async suffix is optional and is ignored for routing purposes.
处理 POST 请求。async 后缀是可选的,出于路由目的而被忽略。
❸ Handles POST requests where the handler route value has the value CustomSearch
处理处理程序路由值值为 CustomSearch 的 POST 请求
Razor Pages can contain any number of page handlers, but only one runs in response to a given request. When the EndpointMiddleware executes a selected Razor Page, it selects a page handler to invoke based on two variables:
Razor Pages 可以包含任意数量的页面处理程序,但只有一个处理程序运行以响应给定请求。当 EndpointMiddleware 执行选定的 Razor 页面时,它会根据两个变量选择要调用的页面处理程序:
• The HTTP verb used in the request (such as GET, POST, or DELETE)
请求中使用的 HTTP 动词 (如 GET、POST 或 DELETE)
• The value of the handler route value
处理程序路由值的值
The handler route value typically comes from a query string value in the request URL, such as /Search?handler=CustomSearch. If you don’t like the look of query strings (I don’t!), you can include the {handler} route parameter in your Razor Page’s route template. For the Search page model in listing 15.2, you could update the page’s directive to
处理程序路由值通常来自请求 URL 中的查询字符串值,例如 /Search?handler=CustomSearch。如果您不喜欢查询字符串的外观(我不喜欢),则可以在 Razor Page 的路由模板中包含 {handler} 路由参数。对于清单 15.2 中的 Search 页面模型,您可以将页面的指令更新为
@page "{handler?}"This would give a complete route template something like "Search/{handler?}", which would match URLs such as /Search and /Search/CustomSearch.
这将提供一个完整的路由模板,类似于 “Search/{handler?}”,它将匹配 /Search 和 /Search/CustomSearch 等 URL。
The EndpointMiddleware uses the handler route value and the HTTP verb together with a standard naming convention to identify which page handler to execute, as shown in figure 15.2. The handler parameter is optional and is typically provided as part of the request’s query string or as a route parameter, as described earlier. The async suffix is also optional and is often used when the handler uses asynchronous programming constructs such as Task or async/await.
EndpointMiddleware 使用处理程序路由值和 HTTP 动词以及标准命名约定来标识要执行的页面处理程序,如图 15.2 所示。handler 参数是可选的,通常作为请求的查询字符串的一部分或作为路由参数提供,如前所述。async 后缀也是可选的,当处理程序使用异步编程构造(如 Task 或 async/await)时,通常会使用该后缀。
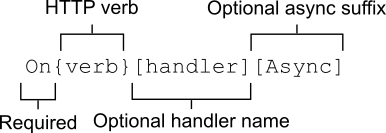
Figure 15.2 Razor Page handlers are matched to a request based on the HTTP verb and the optional handler parameter.
图 15.2 Razor Page 处理程序根据 HTTP 谓词和可选的 handler 参数与请求匹配。
NOTE The async suffix naming convention is suggested by Microsoft, though it is unpopular with some developers. NServiceBus provides a reasoned argument against it here (along with Microsoft’s advice): http://mng.bz/e59P.
注意:async 后缀命名约定由 Microsoft 建议,尽管它在某些开发人员中并不受欢迎。NServiceBus 在这里提供了一个合理的反对它的理由(以及 Microsoft 的建议):http://mng.bz/e59P。
Based on this convention, we can now identify what type of request each page handler in listing 15.1 corresponds to:
基于这个约定,我们现在可以确定清单 15.1 中的每个页面处理程序对应于什么类型的请求:
• OnGet—Invoked for GET requests that don’t specify a handler value
OnGet - 针对未指定处理程序值的GET 请求调用
• OnPostAsync—Invoked for POST requests that don’t specify a handler value; returns a Task, so it uses the Async suffix, which is ignored for routing purposes
OnPostAsync - 针对未指定处理程序值的 POST 请求调用;返回一个 Task,因此它使用 Async 后缀,该后缀在路由时被忽略
• OnPostCustomSearch—Invoked for POST requests that specify a handler value of "CustomSearch"
OnPostCustomSearch - 为指定处理程序值“CustomSearch”的 POST 请求调用
The Razor Page in listing 15.1 specifies three handlers, so it can handle only three verb-handler pairs. But what happens if you get a request that doesn’t match these, such as a request using the DELETE verb, a GET request with a nonblank handler value, or a POST request with an unrecognized handler value?
清单 15.1 中的 Razor Page 指定了三个处理程序,因此它只能处理三个谓词处理程序对。但是,如果您收到与这些不匹配的请求,例如使用 DELETE 动词的请求、具有非空处理程序值的 GET 请求或具有无法识别的处理程序值的 POST 请求,会发生什么情况?
For all these cases, the EndpointMiddleware executes an implicit page handler instead. Implicit page handlers contain no logic; they simply render the Razor view. For example, if you sent a DELETE request to the Razor Page in listing 15.1, the EndpointMiddleware would execute an implicit handler. The implicit page handler is equivalent to the following handler code:
对于所有这些情况,EndpointMiddleware 都会执行隐式页面处理程序。隐式页面处理程序不包含任何逻辑;它们只呈现 Razor 视图。例如,如果向清单 15.1 中的 Razor 页面发送了 DELETE 请求,则 EndpointMiddleware 将执行隐式处理程序。隐式页面处理程序等效于以下处理程序代码:
public void OnDelete() { }DEFINITION If a page handler does not match a request’s HTTP verb and handler value, an implicit page handler is executed that renders the associated Razor view. Implicit page handlers take part in model binding and use page filters but execute no logic.
定义:如果页面处理程序与请求的 HTTP 谓词和处理程序值不匹配,则会执行一个隐式页面处理程序,以呈现关联的 Razor 视图。隐式页面处理程序参与模型绑定并使用页面过滤器,但不执行逻辑。
There’s one exception to the implicit page handler rule: if a request uses the HEAD verb, and there is no corresponding OnHead handler, the EndpointMiddleware executes the OnGet handler instead (if it exists).
隐式页面处理程序规则有一个例外:如果请求使用 HEAD 动词,并且没有相应的 OnHead 处理程序,则 EndpointMiddleware 将改为执行 OnGet 处理程序(如果存在)。
NOTE HEAD requests are typically sent automatically by the browser and don’t return a response body. They’re often used for security purposes, as you’ll see in chapter 28.
注意:HEAD 请求通常由浏览器自动发送,不会返回响应正文。它们通常用于安全目的,如第 28 章所示。
Now that you know how a page handler is selected, you can think about how it’s executed.
现在,您知道了如何选择页面处理程序,您可以考虑如何执行它。
15.3 Accepting parameters to page handlers
15.3 接受页面处理程序的参数
In chapter 7 you learned about the intricacies of model binding in minimal API endpoint handlers. Like minimal APIs, Razor Page page handlers can use model binding to easily extract values from the request. You’ll learn the details of Razor Page model binding in chapter 16; in this section you’ll learn about the basic mechanics of Razor Page model binding and the basic options available.
在第 7 章中,您了解了最小 API 端点处理程序中模型绑定的复杂性。与最小 API 一样,Razor Page 页面处理程序可以使用模型绑定轻松地从请求中提取值。您将在第 16 章中了解 Razor Page 模型绑定的详细信息;在本节中,您将了解 Razor Page 模型绑定的基本机制和可用的基本选项。
When working with Razor Pages, you’ll often want to extract values from an incoming request. If the request is for a search page, the request might contain the search term and the page number in the query string. If the request is POSTing a form to your application, such as a user logging in with their username and password, those values may be encoded in the request body. In other cases, there will be no values, such as when a user requests the home page for your application.
使用 Razor Pages 时,通常需要从传入请求中提取值。如果请求针对搜索页面,则请求可能包含查询字符串中的搜索词和页码。如果请求将表单 POST 到您的应用程序,例如用户使用其用户名和密码登录,则这些值可能会在请求正文中编码。在其他情况下,将没有值,例如当用户请求应用程序的主页时。
DEFINITION The process of extracting values from a request and converting them to .NET types is called model binding. I discuss model binding for Razor Pages in detail in chapter 16.
定义:从请求中提取值并将其转换为 .NET 类型的过程称为模型绑定。我在第 16 章中详细讨论了 Razor Pages 的模型绑定。
ASP.NET Core can bind two different targets in Razor Pages:
ASP.NET Core 可以在 Razor Pages 中绑定两个不同的目标:
• Method arguments—If a page handler has method parameters, the arguments are bound and created from values in the request.
方法参数 - 如果页面处理程序具有方法参数,则根据请求中的值绑定和创建参数。
• Properties marked with a [BindProperty] attribute—Any properties on the PageModel marked with this attribute are bound to the request. By default, this attribute does nothing for GET requests.
标有 [BindProperty] 属性的属性 - PageModel 上标有此属性的任何属性都将绑定到请求。默认情况下,此属性对 GET 请求不执行任何作。
Model-bound values can be simple types, such as strings and integers, or they can be complex types, as shown in the following listing. If any of the values provided in the request are not bound to a property or page handler argument, the additional values will go unused.
模型绑定值可以是简单类型,例如字符串和整数,也可以是复杂类型,如下面的清单所示。如果请求中提供的任何值未绑定到 property 或 page handler 参数,则其他值将未使用。
Listing 15.2 Example Razor Page handlers
列表 15.2 示例 Razor Page 处理程序
public class SearchModel : PageModel
{
private readonly SearchService _searchService; ❶
public SearchModel(SearchService searchService) ❶
{ ❶
_searchService = searchService; ❶
} ❶
[BindProperty] ❷
public BindingModel Input { get; set; } ❷
public List<Product> Results { get; set; } ❸
public void OnGet() ❹
{ ❹
} ❹
public IActionResult OnPost(int max) ❺
{
if (ModelState.IsValid) ❻
{ ❻
Results = _searchService.Search(Input.SearchTerm, max); ❻
return Page(); ❻
} ❻
return RedirectToPage("./Index"); ❻
}
}❶ The SearchService is injected from DI for use in page handlers.
SearchService 从 DI 注入,用于页面处理程序。
❷ Properties decorated with the [BindProperty] attribute are model-bound.
使用 [BindProperty] 属性修饰的属性是模型绑定的。
❸ Undecorated properties are not model-bound.
未修饰的属性不受模型限制。
❹ The page handler doesn’t need to check if the model is valid. Returning void renders the view.
页面处理程序不需要检查模型是否有效。返回 void 将呈现视图。
❺ The max parameter is model-bound using values in the request.
max 参数使用请求中的值进行模型绑定。
❻ If the request was not valid, the method indicates the user should be redirected to the Index page.
如果请求无效,该方法指示应将用户重定向到 Index 页面。
In this example, the OnGet handler doesn’t require any parameters, and the method is simple: it returns void, which means the associated Razor view will be rendered. It could also have returned a PageResult; the effect would have been the same. Note that this handler is for HTTP GET requests, so the Input property decorated with [BindProperty] is not bound.
在此示例中,OnGet 处理程序不需要任何参数,方法很简单:它返回 void,这意味着将呈现关联的 Razor 视图。它还可能返回 PageResult;效果是一样的。请注意,此处理程序用于 HTTP GET 请求,因此不会绑定用 [BindProperty] 修饰的 Input 属性。
Tip To bind properties for GET requests too, use the SupportsGet property of the attribute, as in [BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)].
提示:若要同时绑定 GET 请求的属性,请使用该属性的 SupportsGet 属性,如 [BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)] 中所示。
The OnPost handler, conversely, accepts a parameter max as an argument. In this case it’s a simple type, int, but it could also be a complex object. Additionally, as this handler corresponds to an HTTP POST request, the Input property is also model-bound to the request.
相反,OnPost 处理程序接受参数 max 作为参数。在本例中,它是一个简单类型 int,但它也可能是一个复杂对象。此外,由于此处理程序对应于 HTTP POST 请求,因此 Input 属性也与请求模型绑定。
NOTE Unlike most .NET classes, you can’t use method overloading to have multiple page handlers on a Razor Page with the same name.
注意:与大多数 .NET 类不同,不能使用方法重载在 Razor 页面上拥有多个同名页面处理程序。
When a page handler uses model-bound properties or parameters, it should always check that the provided model is valid using ModelState.IsValid. The ModelState property is exposed as a property on the base PageModel class and can be used to check that all the bound properties and parameters are valid. You’ll see how the process works in chapter 16 when you learn about validation.
当页面处理程序使用模型绑定属性或参数时,它应始终使用 ModelState.IsValid 检查提供的模型是否有效。ModelState 属性作为基 PageModel 类上的属性公开,可用于检查所有绑定的属性和参数是否有效。当您了解验证时,您将在第 16 章中看到该过程的工作原理。
Once a page handler establishes that the arguments provided to a page handler method are valid, it can execute the appropriate business logic and handle the request. In the case of the OnPost handler, this involves calling the injected SearchService and setting the result on the Results property. Finally, the handler returns a PageResult by calling the helper method on the PageModel base class:
一旦页面处理程序确定提供给页面处理程序方法的参数有效,它就可以执行相应的业务逻辑并处理请求。对于 OnPost 处理程序,这涉及调用注入的 SearchService 并在 Results 属性上设置结果。最后,处理程序通过调用 PageModel 基类上的帮助程序方法返回 PageResult:
return Page();If the model isn’t valid, as indicated by ModelState.IsValid, you don’t have any results to display! In this example, the action returns a RedirectToPageResult using the RedirectToPage() helper method. When executed, this result sends a 302 Redirect response to the user, which will cause their browser to navigate to the Index Razor Page.
如果模型无效(如 ModelState.IsValid 所示),则没有任何结果可显示!在此示例中,该作使用 RedirectToPage() 帮助程序方法返回 RedirectToPageResult。执行时,此结果会向用户发送 302 Redirect 响应,这将导致其浏览器导航到 Index Razor 页面。
Note that the OnGet method returns void in the method signature, whereas the OnPost method returns an IActionResult. This is required in the OnPost method to allow the C# to compile (as the Page() and RedirectToPage() helper methods return different types), but it doesn’t change the final behavior of the methods. You could easily have called Page() in the OnGet method and returned an IActionResult, and the behavior would be identical.
请注意,OnGet 方法在方法签名中返回 void,而 OnPost 方法返回 IActionResult。这在 OnPost 方法中是必需的,以允许 C# 进行编译(因为 Page() 和 RedirectToPage() 帮助程序方法返回不同的类型),但它不会更改方法的最终行为。您可以轻松地在 OnGet 方法中调用 Page() 并返回 IActionResult,并且行为是相同的。
Tip If you’re returning more than one type of result from a page handler, you’ll need to ensure that your method returns an IActionResult.
提示:如果要从页面处理程序返回多种类型的结果,则需要确保方法返回 IActionResult。
In listing 15.2 I used Page() and RedirectToPage() methods to generate the return value. IActionResult instances can be created and returned using the normal new syntax of C#:
在清单 15.2 中,我使用了 Page() 和 RedirectToPage() 方法来生成返回值。可以使用 C# 的常规新语法创建和返回 IActionResult 实例:
return new PageResult()However, the Razor Pages PageModel base class also provides several helper methods for generating responses, which are thin wrappers around the new syntax. It’s common to use the Page() method to generate an appropriate PageResult, the RedirectToPage() method to generate a RedirectToPageResult, or the NotFound() method to generate a NotFoundResult.
但是,Razor Pages PageModel 基类还提供了多个用于生成响应的帮助程序方法,这些方法是新语法的精简包装器。通常使用 Page() 方法生成相应的 PageResult,使用 RedirectToPage() 方法生成 RedirectToPageResult,或使用 NotFound() 方法生成 NotFoundResult。
Tip Most IActionResult implementations have a helper method on the base PageModel class. They’re typically named Type, and the result generated is called TypeResult. For example, the StatusCode() method returns a StatusCodeResult instance.
提示:大多数 IActionResult 实现在基 PageModel 类上都有一个帮助程序方法。它们通常命名为 Type,生成的结果称为 TypeResult。例如,StatusCode() 方法返回 StatusCodeResult 实例。
In the next section we’ll look in more depth at some of the common IActionResult types.
在下一节中,我们将更深入地了解一些常见的 IActionResult 类型。
15.4 Returning IActionResult responses
15.4 返回 IActionResult 响应
In the previous section, I emphasized that page handlers decide what type of response to return, but they don’t generate the response themselves. It’s the IActionResult returned by a page handler that, when executed by the Razor Pages infrastructure using the view engine, generates the response.
在上一节中,我强调了页面处理程序决定返回哪种类型的响应,但它们自己不会生成响应。页面处理程序返回的 IActionResult 在由使用视图引擎的 Razor Pages 基础结构执行时,会生成响应。
Warning Note that the interface type is IActionResult not IResult. IResult is used in minimal APIs and should generally be avoided in Razor Pages (and MVC controllers). In .NET 7, IResult types returned from Razor Pages or MVC controllers execute as expected, but they don’t have all the same features as IActionResult, so you should favor IActionResult in Razor Pages.
警告:请注意,接口类型是 IActionResult 而不是 IResult。IResult 用于最小的 API,通常应避免在 Razor Pages(和 MVC 控制器)中使用。在 .NET 7 中,从 Razor Pages 或 MVC 控制器返回的 IResult 类型按预期执行,但它们不具有与 IActionResult 相同的所有功能,因此你应该在 Razor Pages 中首选 IActionResult。
IActionResults are a key part of the MVC design pattern. They separate the decision of what sort of response to send from the generation of the response. This allows you to test your action method logic to confirm that the right sort of response is sent for a given input. You can then separately test that a given IActionResult generates the expected HTML, for example.
IActionResults 是 MVC 设计模式的关键部分。它们将发送哪种响应的决定与响应的生成分开。这允许您测试作方法逻辑,以确认为给定输入发送了正确类型的响应。例如,您可以单独测试给定的 IActionResult 是否生成了预期的 HTML。
ASP.NET Core has many types of IActionResult, such as
ASP.NET Core 具有多种类型的 IActionResult,例如
• PageResult—Generates an HTML view for the associated page in Razor Pages and returns a 200 HTTP response.
PageResult - 在 Razor Pages 中为关联页面生成 HTML 视图,并返回 200 HTTP 响应。
• ViewResult—Generates an HTML view for a given Razor view when using MVC controllers and returns a 200 HTTP response.
ViewResult - 使用 MVC 控制器时,为给定 Razor 视图生成 HTML 视图,并返回 200 HTTP 响应。
• PartialViewResult—Renders part of an HTML page using a given Razor view and returns a 200 HTTP result; typically used with MVC controllers and AJAX requests.
PartialViewResult - 使用给定的 Razor 视图呈现 HTML 页面的一部分,并返回 200 HTTP 结果;通常用于 MVC 控制器和 AJAX 请求。
• RedirectToPageResult—Sends a 302 HTTP redirect response to automatically send a user to another page.
RedirectToPageResult - 发送 302 HTTP 重定向响应以自动将用户发送到其他页面。
• RedirectResult—Sends a 302 HTTP redirect response to automatically send a user to a specified URL (doesn’t have to be a Razor Page).
RedirectResult - 发送 302 HTTP 重定向响应以自动将用户发送到指定的 URL (不必是 Razor 页面)。
• FileResult—Returns a file as the response. This is a base class with several derived types:
FileResult - 返回文件作为响应。这是一个具有多个派生类型的基类:
• • FileContentResult—Returns a byte[] as a file response to the browser
FileContentResult - 返回 byte[] 作为对浏览器的文件响应
• • FileStreamResult—Returns the contents of a Stream as a file response to the browser
FileStreamResult - 将 Stream 的内容作为文件响应返回给浏览器
• • PhysicalFileResult—Returns the contents of a file on disk as a file response to the browser
PhysicalFileResult - 将磁盘上文件的内容作为文件响应返回给浏览器
• ContentResult—Returns a provided string as the response.
ContentResult - 返回提供的字符串作为响应。
• StatusCodeResult—Sends a raw HTTP status code as the response, optionally with associated response body content.
StatusCodeResult - 发送原始 HTTP 状态代码作为响应,可选择发送关联的响应正文内容。
• NotFoundResult—Sends a raw 404 HTTP status code as the response.
NotFoundResult - 发送原始 404 HTTP 状态代码作为响应。
Each of these, when executed by Razor Pages, generates a response to send back through the middleware pipeline and out to the user.
当 Razor Pages 执行时,每个作都会生成一个响应,以通过中间件管道发送回给用户。
Tip When you’re using Razor Pages, you generally won’t use some of these action results, such as ContentResult and StatusCodeResult. It’s good to be aware of them, though, as you will likely use them if you are building Web APIs with MVC controllers, as you’ll see in chapter 20.
提示:使用 Razor Pages 时,通常不会使用其中一些作结果,例如 ContentResult 和 StatusCodeResult。不过,了解它们是件好事,因为如果你正在使用 MVC 控制器构建 Web API,你可能会使用它们,如第 20 章所示。
In sections 15.4.1–15.4.3 I give a brief description of the most common IActionResult types that you’ll use with Razor Pages.
在第 15.4.1–15.4.3 节中,我简要介绍了您将用于 Razor Pages 的最常见 IActionResult 类型。
15.4.1 PageResult and RedirectToPageResult
15.4.1 PageResult 和 RedirectToPageResult
When you’re building a traditional web application with Razor Pages, usually you’ll be using PageResult, which generates an HTML response from the Razor Page’s associated Razor view. We’ll look at how this happens in detail in chapter 17.
使用 Razor Pages 构建传统 Web 应用程序时,通常会使用 PageResult,它会从 Razor Page 的关联 Razor 视图生成 HTML 响应。我们将在第 17 章详细看看这是如何发生的。
You’ll also commonly use the various redirect-based results to send the user to a new web page. For example, when you place an order on an e-commerce website, you typically navigate through multiple pages, as shown in figure 15.3. The web application sends HTTP redirects whenever it needs you to move to a different page, such as when a user submits a form. Your browser automatically follows the redirect requests, creating a seamless flow through the checkout process.
您通常还会使用各种基于重定向的结果将用户发送到新网页。例如,当您在电子商务网站上下订单时,通常会浏览多个页面,如图 15.3 所示。每当 Web 应用程序需要您移动到其他页面时(例如,当用户提交表单时),它都会发送 HTTP 重定向。您的浏览器会自动遵循重定向请求,从而在结帐过程中创建无缝流程。
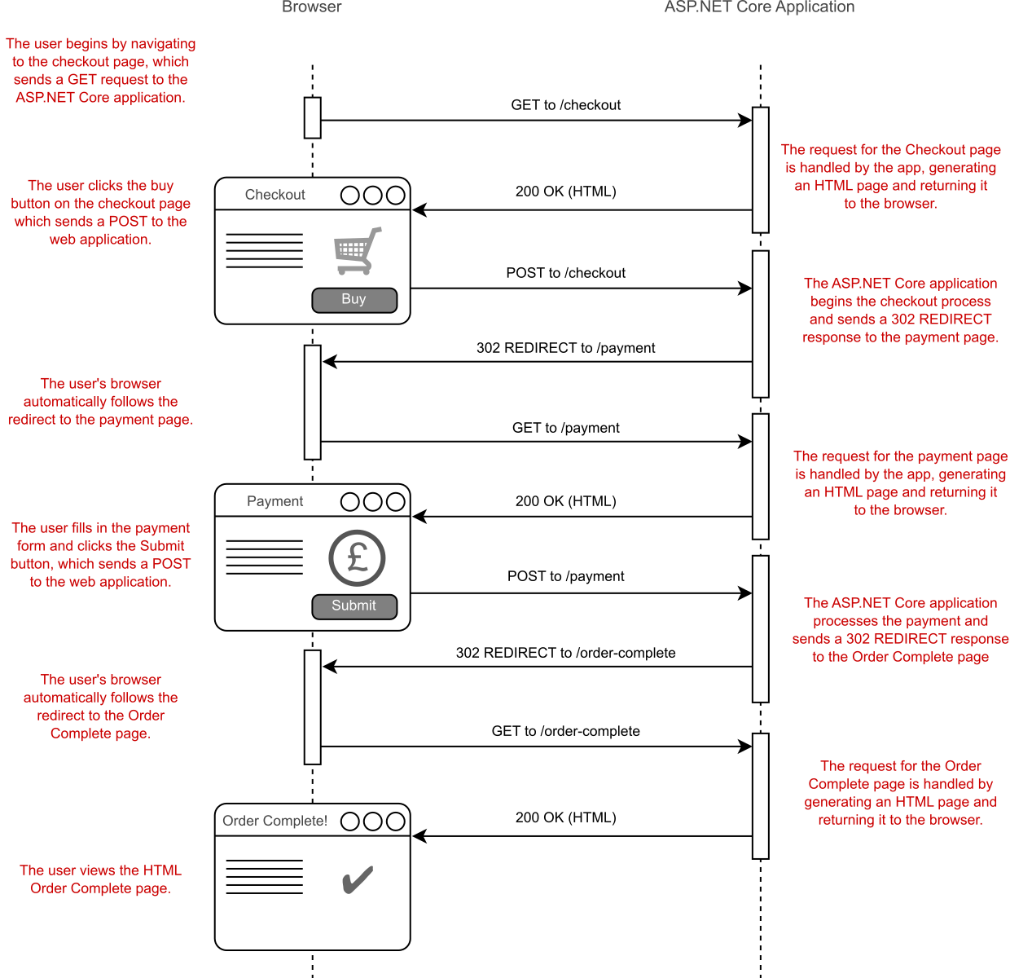
Figure 15.3 A typical POST, REDIRECT, GET flow through a website. A user sends their shopping basket to a checkout page, which validates its contents and redirects to a payment page without the user’s having to change the URL manually.
图 15.3 典型的 POST、REDIRECT、GET 流经网站。用户将他们的购物篮发送到结帐页面,该页面会验证其内容并重定向到支付页面,而无需用户手动更改 URL。
In this flow, whenever you return HTML you use a PageResult; when you redirect to a new page, you use a RedirectToPageResult.
在此流程中,无论何时返回 HTML,您都会使用 PageResult;当您重定向到新页面时,您将使用 RedirectToPageResult。
Tip Razor Pages are generally designed to be stateless, so if you want to persist data between multiple pages, you need to place it in a database or similar store. If you want to store data for a single request, you may be able to use TempData, which stores small amounts of data in cookies for a single request. See the documentation for details: http://mng.bz/XdXp.
提示:Razor 页面通常设计为无状态的,因此如果要在多个页面之间保存数据,则需要将其放置在数据库或类似存储中。如果要存储单个请求的数据,则可以使用 TempData,它将少量数据存储在单个请求的 Cookie 中。有关详细信息,请参阅文档:http://mng.bz/XdXp。
15.4.2 NotFoundResult and StatusCodeResult
15.4.2 NotFoundResult 和 StatusCodeResult
As well as sending HTML and redirect responses, you’ll occasionally need to send specific HTTP status codes. If you request a page for viewing a product on an e-commerce application, and that product doesn’t exist, a 404 HTTP status code is returned to the browser, and you’ll typically see a “Not found” web page. Razor Pages can achieve this behavior by returning a NotFoundResult, which returns a raw 404 HTTP status code. You could achieve a similar result using StatusCodeResult and setting the status code returned explicitly to 404.
除了发送 HTML 和重定向响应外,您有时还需要发送特定的 HTTP 状态代码。如果您请求一个页面来查看电子商务应用程序上的产品,但该产品不存在,则会向浏览器返回 404 HTTP 状态代码,并且您通常会看到“未找到”网页。Razor Pages 可以通过返回 NotFoundResult 来实现此行为,该结果返回原始 404 HTTP 状态代码。您可以使用 StatusCodeResult 并将返回的状态代码显式设置为 404 来实现类似的结果。
Note that NotFoundResult doesn’t generate any HTML; it only generates a raw 404 status code and returns it through the middleware pipeline. This generally isn’t a great user experience, as the browser typically displays a default page, such as that shown in figure 15.4.
请注意,NotFoundResult 不会生成任何 HTML;它只生成一个原始的 404 状态码,并通过中间件管道返回。这通常不是很好的用户体验,因为浏览器通常会显示默认页面,如图 15.4 所示。
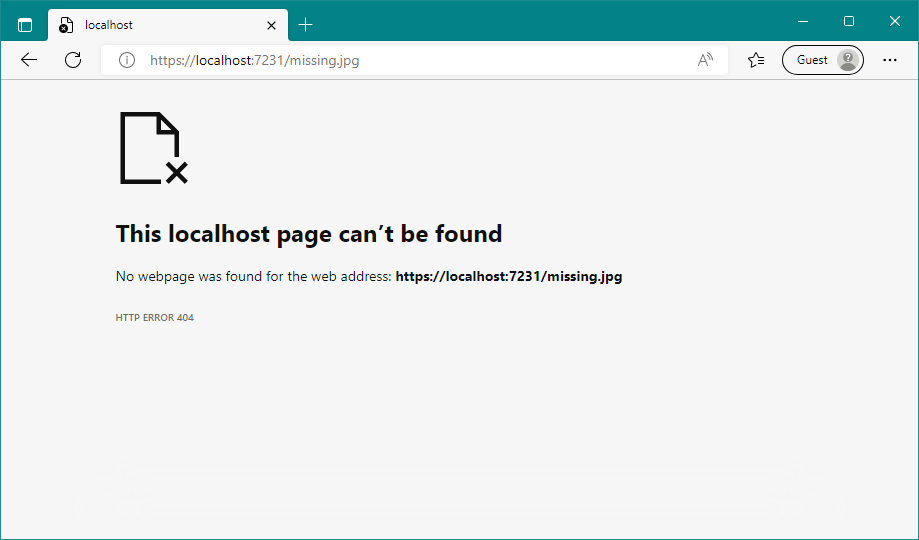
Figure 15.4 If you return a raw 404 status code without any HTML, the browser will render a generic default page instead. The message is of limited utility to users and may leave many of them confused or thinking that your web application is broken.
图 15.4 如果返回不带任何 HTML 的原始 404 状态代码,浏览器将呈现通用的默认页面。该消息对用户的实用性有限,可能会让许多人感到困惑或认为您的 Web 应用程序已损坏。
Returning raw status codes is fine when you’re building an API, but for a Razor Pages application, this is rarely good enough. In section 15.5 you’ll learn how you can intercept this raw 404 status code after it’s been generated and provide a user-friendly HTML response for it instead.
在构建 API 时,返回原始状态代码是可以的,但对于 Razor Pages 应用程序,这很少足够好。在 Section 15.5 中,您将学习如何在生成原始 404 状态代码后拦截它,并为其提供用户友好的 HTML 响应。
15.5 Handler status codes with StatusCodePagesMiddleware
15.5 使用 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 的处理程序状态码
In chapter 4 we discussed error handling middleware, which is designed to catch exceptions generated anywhere in your middleware pipeline, catch them, and generate a user-friendly response. In this section you’ll learn about an analogous piece of middleware that intercepts error HTTP status codes: StatusCodePagesMiddleware.
在第 4 章中,我们讨论了错误处理中间件,它旨在捕获中间件管道中任何位置生成的异常,捕获它们,并生成用户友好的响应。在本节中,您将了解一个类似的中间件,用于拦截错误 HTTP 状态代码:StatusCodePagesMiddleware。
Your Razor Pages application can return a wide range of HTTP status codes that indicate some sort of error state. You’ve seen previously that a 500 “server error” is sent when an exception occurs and isn’t handled and that a 404 “file not found” error is sent when you return a NotFoundResult from a page handler. 404 errors are particularly common, often occurring when a user enters an invalid URL.
Razor Pages 应用程序可以返回各种 HTTP 状态代码,这些代码指示某种错误状态。您之前已经看到,当发生异常且未得到处理时,会发送 500 “server error” ,当您从页面处理程序返回 NotFoundResult 时,会发送 404 “file not found” 错误。404 错误特别常见,通常在用户输入无效的 URL 时发生。
Tip 404 errors are often used to indicate that a specific requested object was not found. For example, a request for the details of a product with an ID of 23 might return a 404 if no such product exists. They’re also generated automatically if no endpoint in your application matches the request URL.
Tip: 404 错误通常用于指示未找到特定请求的对象。例如,如果不存在 ID 为 23 的产品的详细信息,则请求 ID 为 23 的产品可能会返回 404。如果应用程序中没有终端节点与请求 URL 匹配,系统也会自动生成这些 URL。
Returning “raw” status codes without additional content is generally OK if you’re building a minimal API or web API application. But as mentioned before, for apps consumed directly by users such as Razor Pages apps, this can result in a poor user experience. If you don’t handle these status codes, users will see a generic error page, as you saw in figure 15.4, which may leave many confused users thinking your application is broken. A better approach is to handle these error codes and return an error page that’s in keeping with the rest of your application or at least doesn’t make your application look broken.
如果您正在构建最小的 API 或 Web API 应用程序,则返回不带额外内容的“原始”状态代码通常是可以的。但如前所述,对于用户直接使用的应用程序(如 Razor Pages 应用程序),这可能会导致用户体验不佳。如果你不处理这些状态码,用户将看到一个通用的错误页面,如图 15.4 所示,这可能会让许多困惑的用户认为你的应用程序坏了。更好的方法是处理这些错误代码并返回一个错误页面,该页面与应用程序的其余部分保持一致,或者至少不会使您的应用程序看起来损坏。
Microsoft provides StatusCodePagesMiddleware for handling this use case. As with all error handling middleware, you should add it early in your middleware pipeline, as it will handle only errors generated by later middleware components.
Microsoft 提供了 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 来处理此用例。与所有错误处理中间件一样,您应该在中间件管道的早期添加它,因为它将仅处理后续中间件组件生成的错误。
You can use the middleware several ways in your application. The simplest approach is to add the middleware to your pipeline without any additional configuration, using
您可以在应用程序中以多种方式使用中间件。最简单的方法是将中间件添加到您的管道中,无需任何其他配置,使用
app.UseStatusCodePages();With this method, the middleware intercepts any response that has an HTTP status code that starts with 4xx or 5xx and has no response body. For the simplest case, where you don’t provide any additional configuration, the middleware adds a plain-text response body, indicating the type and name of the response, as shown in figure 15.5. This is arguably worse than the default message at this point, but it is a starting point for providing a more consistent experience to users.
使用此方法,中间件会拦截 HTTP 状态代码以 4xx 或 5xx 开头且没有响应正文的任何响应。对于最简单的情况,如果您不提供任何其他配置,中间件会添加一个纯文本响应正文,指示响应的类型和名称,如图 15.5 所示。这可以说比此时的默认消息更糟糕,但它是为用户提供更一致体验的起点。
Figure 15.5 Status code error page for a 404 error. You generally won’t use this version of the middleware in production, as it doesn’t provide a great user experience, but it demonstrates that the error codes are being intercepted correctly.
图 15.5 404 错误的状态代码错误页面。您通常不会在生产环境中使用此版本的中间件,因为它不会提供出色的用户体验,但它表明错误代码被正确拦截。
A more typical approach to using StatusCodePagesMiddleware in production is to reexecute the pipeline when an error is captured, using a similar technique to the ExceptionHandlerMiddleware. This allows you to have dynamic error pages that fit with the rest of your application. To use this technique, replace the call to UseStatusCodePages with the following extension method:
在生产环境中使用 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 的更典型方法是在捕获错误时重新执行管道,使用与 ExceptionHandlerMiddleware 类似的技术。这允许你拥有适合应用程序其余部分的动态错误页面。若要使用此技术,请将对 UseStatusCodePages 的调用替换为以下扩展方法:
app.UseStatusCodePagesWithReExecute("/{0}");This extension method configures StatusCodePagesMiddleware to reexecute the pipeline whenever a 4xx or 5xx response code is found, using the provided error handling path. This is similar to the way ExceptionHandlerMiddleware reexecutes the pipeline, as shown in figure 15.6.
此扩展方法将 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 配置为在找到 4xx 或 5xx 响应代码时,使用提供的错误处理路径重新执行管道。这类似于 ExceptionHandlerMiddleware 重新执行管道的方式,如图 15.6 所示。
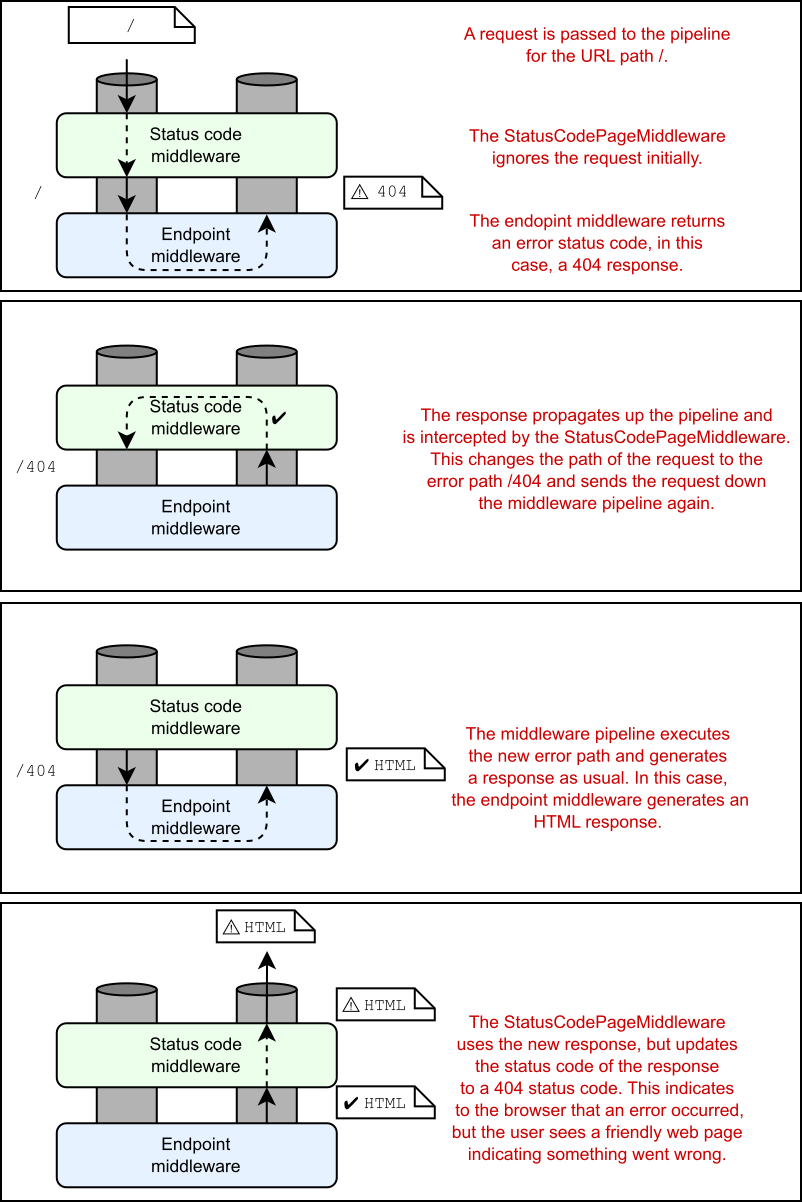
Figure 15.6 StatusCodePagesMiddleware reexecuting the pipeline to generate an HTML body for a 404 response. A request to the / path returns a 404 response, which is handled by the status code middleware. The pipeline is reexecuted using the /404 path to generate the HTML response.
图 15.6 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 重新执行管道以生成 404 响应的 HTML 正文。对 / 路径的请求将返回 404 响应,该响应由状态代码中间件处理。使用 /404 路径重新执行管道以生成 HTML 响应。
Note that the error handling path "/{0}" contains a format string token, {0}. When the path is reexecuted, the middleware replaces this token with the status code number. For example, a 404 error would reexecute the /404 path. The handler for the path (typically a Razor Page, but it can be any endpoint) has access to the status code and can optionally tailor the response, depending on the status code. You can choose any error handling path as long as your application knows how to handle it.
请注意,错误处理路径 “/{0}” 包含格式字符串标记 {0}。重新执行路径时,中间件会将此令牌替换为状态代码编号。例如,404 错误将重新执行 /404 路径。路径的处理程序(通常是 Razor Page,但可以是任何终结点)有权访问状态代码,并且可以根据状态代码选择性地定制响应。您可以选择任何错误处理路径,只要您的应用程序知道如何处理它。
With this approach in place, you can create different error pages for different error codes, such as the 404-specific error page shown in figure 15.7. This technique ensures that your error pages are consistent with the rest of your application, including any dynamically generated content, while also allowing you to tailor the message for common errors.
使用这种方法,您可以为不同的错误代码创建不同的错误页面,例如图 15.7 中所示的特定于 404 的错误页面。此技术可确保错误页面与应用程序的其余部分(包括任何动态生成的内容)保持一致,同时还允许您针对常见错误定制消息。
Figure 15.7 An error status code page for a missing file. When an error code is detected (in this case, a 404 error), the middleware pipeline is reexecuted to generate the response. This allows dynamic portions of your web page to remain consistent on error pages.
图 15.7 缺失文件的错误状态代码页面。当检测到错误代码(在本例中为 404 错误)时,将重新执行中间件管道以生成响应。这允许网页的动态部分在错误页面上保持一致。
Warning As I mentioned in chapter 4, if your error handling path generates an error, the user will see a generic browser error. To mitigate this, it’s often better to use a static error page that will always work rather than a dynamic page that risks throwing more errors.
警告:正如我在第 4 章中提到的,如果你的错误处理路径产生了一个错误,用户将看到一个通用的浏览器错误。为了缓解这种情况,通常最好使用始终有效的静态错误页面,而不是冒着引发更多错误的动态页面。
The UseStatusCodePagesWithReExecute() method is great for returning a friendly error page when something goes wrong in a request, but there’s a second way to use the StatusCodePagesMiddleware. Instead of reexecuting the pipeline to generate the error response, you can redirect the browser to the error page instead, by calling
UseStatusCodePagesWithReExecute() 方法非常适合在请求出错时返回友好的错误页面,但还有第二种方法可以使用 StatusCodePagesMiddleware。您可以通过调用
app.UseStatusCodePagesWithRedirects("/{0}");As for the reexecute version, this method takes a format string that defines the URL to generate the response. However, whereas the reexecute version generates the error response for the original request, the redirect version returns a 302 response initially, directing the browser to send a second request, this time for the error URL, as shown in figure 15.8. This second request generates the error page response, returning it with a 200 status code.
对于 reexecute 版本,此方法采用定义 URL 以生成响应的格式字符串。但是,reexecute 版本为原始请求生成错误响应,而重定向版本最初返回 302 响应,指示浏览器发送第二个请求,这次是针对错误 URL,如图 15.8 所示。第二个请求生成错误页面响应,并返回 200 状态代码。
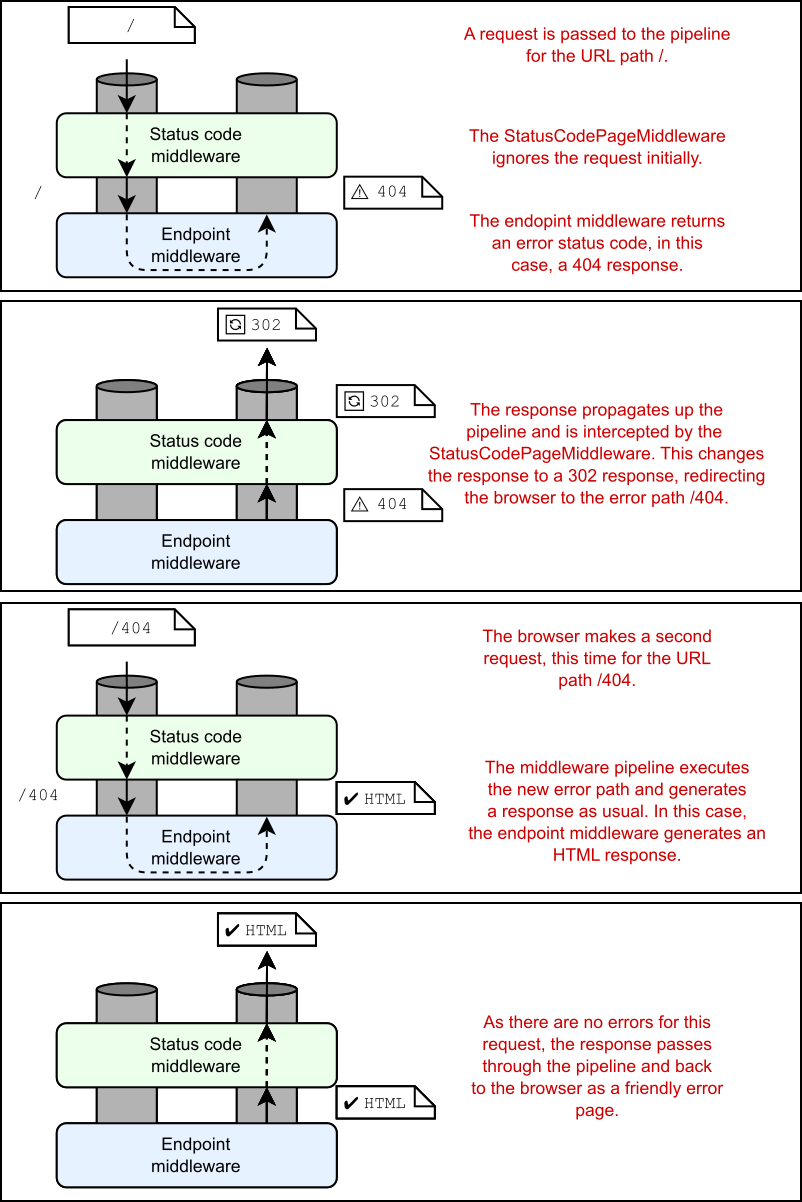
Figure 15.8 StatusCodePagesMiddleware returning redirects to generate error pages. A request to the / path returns a 404 response, which is intercepted by the status code middleware and converted to a 302 response. The browser makes a second request using the /404 path to generate the HTML response.
图 15.8 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 返回重定向以生成错误页面。对 / 路径的请求返回 404 响应,该响应被状态代码中间件拦截并转换为 302 响应。浏览器使用 /404 路径发出第二个请求以生成 HTML 响应。
Whether you use the reexecute or redirect method, the browser ultimately receives essentially the same HTML. However, there are some important differences:
无论您使用 reexecute 还是 redirect 方法,浏览器最终都会收到基本相同的 HTML。但是,存在一些重要的差异:
• With the reexecute approach, the original status code (such as a 404) is preserved. The browser sees the error page HTML as the response to the original request. If the user refreshes the page, the browser makes a second request for the original path.
使用重新执行方法时,将保留原始状态代码 (如 404)。浏览器将错误页面 HTML 视为对原始请求的响应。如果用户刷新页面,浏览器将对原始路径发出第二个请求。
• With the redirect approach, the original status code is lost. The browser treats the redirect and second request as two separate requests and doesn’t “know” about the error. If the user refreshes the page, the browser makes a request for the same error path; it doesn’t resend the original request.
使用重定向方法时,原始状态代码将丢失。浏览器将重定向和第二个请求视为两个单独的请求,并且“不知道”错误。如果用户刷新页面,浏览器会请求相同的错误路径;它不会重新发送原始请求。
In most cases, I find the reexecute approach to be more useful, as it preserves the original error and typically has the behavior that users expect. There may be some cases where the redirect approach is useful, however, such as when an entirely different application generates the error page.
在大多数情况下,我发现 reexecute 方法更有用,因为它保留了原始错误,并且通常具有用户期望的行为。但是,在某些情况下,重定向方法可能很有用,例如,当完全不同的应用程序生成错误页面时。
Tip Favor using UseStatusCodePagesWithReExecute over the redirect approach when the same app is generating the error page HTML for your app.
提示:当同一应用程序为您的应用程序生成错误页面 HTML 时,优先使用 UseStatusCodePagesWithReExecute 而不是重定向方法。
You can use StatusCodePagesMiddleware in combination with other exception handling middleware by adding both to the pipeline. StatusCodePagesMiddleware modifies the response only if no response body has been written. So if another component, such as ExceptionHandlerMiddleware, returns a message body along with an error code, it won’t be modified.
您可以将 StatusCodePagesMiddleware 与其他异常处理中间件结合使用,方法是将两者添加到管道中。StatusCodePagesMiddleware 仅在未写入响应正文时修改响应。因此,如果另一个组件(比如 ExceptionHandlerMiddleware)返回消息正文和错误代码,则不会对其进行修改。
NOTE StatusCodePagesMiddleware has additional overloads that let you execute custom middleware when an error occurs instead of reexecuting the middleware pipeline. You can read about this approach at http://mng.bz/0K66.
注意:StatusCodePagesMiddleware 具有额外的重载,允许您在发生错误时执行自定义中间件,而不是重新执行中间件管道。您可以在 http://mng.bz/0K66 上阅读有关此方法的信息。
Error handling is essential when developing any web application; errors happen, and you need to handle them gracefully. The StatusCodePagesMiddleware is practically a must-have for any production Razor Pages app.
在开发任何 Web 应用程序时,错误处理都是必不可少的;错误会发生,您需要妥善处理它们。StatusCodePagesMiddleware 实际上是任何生产 Razor Pages 应用的必备工具。
In chapter 16 we’ll dive into model binding. You’ll see how the route values generated during routing are bound to your page handler parameters, and perhaps more important, how to validate the values you’re provided.
在第 16 章中,我们将深入探讨模型绑定。您将看到路由期间生成的路由值如何绑定到您的页面处理程序参数,也许更重要的是,如何验证您提供的值。
15.6 Summary
15.6 总结
A Razor Page page handler is the method in the Razor Page PageModel class that is executed when a Razor Page handles a request.
Razor Page 页面处理程序是 Razor Page PageModel 类中的方法,在 Razor Page 处理请求时执行。
Page handlers should ensure that the incoming request is valid, call in to the appropriate domain services to handle the request, and then choose the kind of response to return. They typically don’t generate the response directly; instead, they describe how to generate the response.
页面处理程序应确保传入请求有效,调用相应的域服务以处理请求,然后选择要返回的响应类型。它们通常不会直接生成响应;相反,它们描述了如何生成响应。
Page handlers should generally delegate to services to handle the business logic required by a request instead of performing the changes themselves. This ensures a clean separation of concerns that aids testing and improves application structure.
页面处理程序通常应委托给服务来处理请求所需的业务逻辑,而不是自行执行更改。这确保了关注点的清晰分离,从而有助于测试并改进应用程序结构。
When a Razor Page is executed, a single page handler is invoked based on the HTTP verb of the request and the value of the handler route value. If no page handler is found, an “implicit” handler is used instead, simply rendering the content of the Razor Page.
执行 Razor 页面时,将根据请求的 HTTP 谓词和处理程序路由值的值调用单个页面处理程序。如果未找到页面处理程序,则改用“隐式”处理程序,只呈现 Razor Page 的内容。
Page handlers can have parameters whose values are taken from properties of the incoming request in a process called model binding. Properties decorated with [BindProperty] can also be bound to the request. These are the canonical ways of reading values from the HTTP request inside your Razor Page.
页面处理程序可以具有参数,这些参数的值取自称为模型绑定的进程中传入请求的属性。使用 [BindProperty] 修饰的属性也可以绑定到请求。这些是从 Razor 页面内的 HTTP 请求中读取值的规范方法。
By default, properties decorated with [BindProperty] are not bound for GET requests. To enable binding, use [BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)].
默认情况下,使用 [BindProperty] 修饰的属性不会绑定到 GET 请求。若要启用绑定,请使用 [BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)]。
Page handlers can return a PageResult or void to generate an HTML response. The Razor Page infrastructure uses the associated Razor view to generate the HTML and returns a 200 OK response.
页面处理程序可以返回 PageResult 或 void 以生成 HTML 响应。Razor 页面基础结构使用关联的 Razor 视图生成 HTML 并返回 200 OK 响应。
You can send users to a different Razor Page using a RedirectToPageResult. It’s common to send users to a new page as part of the POST-REDIRECT-GET flow for handling user input via forms
您可以使用 RedirectToPageResult 将用户发送到不同的 Razor 页面。将用户发送到新页面通常是通过 POST-REDIRECT-GET 流程处理用户输入的一部分
The PageModel base class exposes many helper methods for creating an IActionResult, such as Page() which creates a PageResult, and RedirectToPage() which creates a RedirectToPageResult. These methods are simple wrappers around calling new on the corresponding IActionResult type.
PageModel 基类公开了许多用于创建 IActionResult 的帮助程序方法,例如创建 PageResult 的 Page() 和用于创建 RedirectToPageResult 的 RedirectToPage()。这些方法是对相应的 IActionResult 类型调用 new 的简单包装器。
StatusCodePagesMiddleware lets you provide user-friendly custom error handling messages when the pipeline returns a raw error response status code. This is important for providing a consistent user experience when status code errors are returned, such as 404 errors when a URL is not matched to an endpoint.
StatusCodePagesMiddleware 允许您在管道返回原始错误响应状态代码时提供用户友好的自定义错误处理消息。这对于在返回状态代码错误时提供一致的用户体验非常重要,例如,当 URL 与终端节点不匹配时出现 404 错误。